Seamlessly Onboard VLAN-Backed Workloads into Your VCF Private Cloud with NSX
Table of contents
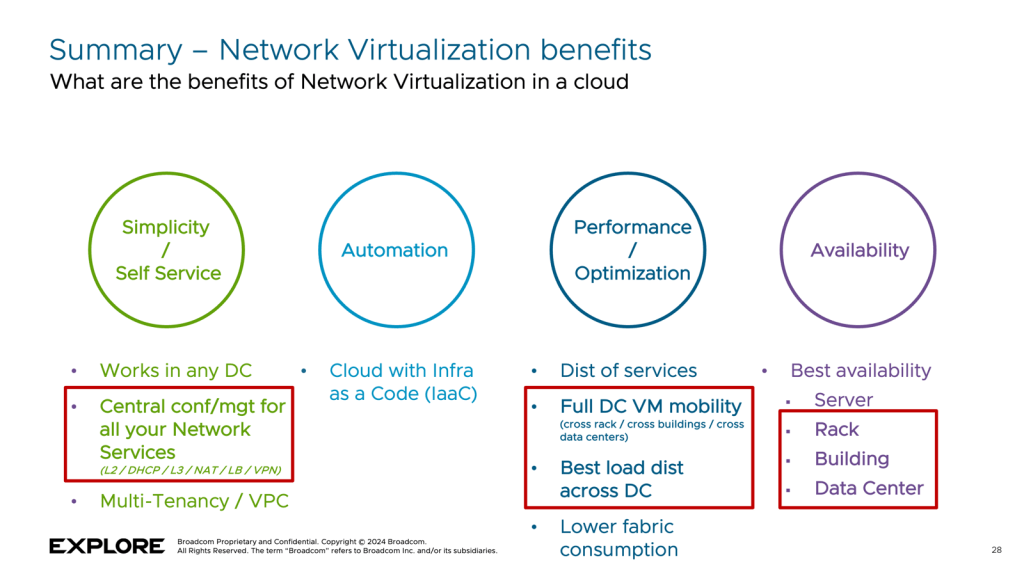
Summary
- Seamless Migration: Existing VLAN-based applications can be easily moved to VCF Networking without disruption.
- Immediate Benefits: Gain centralized management, automation, performance optimization, and high availability.
- Enhanced Capabilities after migration:
- Integrated Load Balancing
- Micro-Segmentation for improved security
- VM mobility across buildings and data centers
- Built-in resilience to rack, building, or data center failures
Presentation
Before adopting Network Virtualization, customers had already deployed applications in their data centers, and many of those applications may still be running there today.
By transitioning from traditional VLANs to Network Virtualization with VCF Networking, these applications can immediately benefit from a range of powerful features, including simplicity, self-service, automation, performance optimization, and high availability.
Key benefits of migrating to VCF Networking include:
- Central Configuration and Management
Seamless control of all your network services such as Switching, DHCP, Routing, NAT, Load Balancing, and VPN. - Full VM Mobility
Live vMotion of virtual machines (VMs) between any ESX hypervisors within a data center — or even across multiple data centers — is fully supported. - Superior High Availability
Applications gain resilience not just against rack failures, but also against complete building or data center outages.
Demo
In the demo below, you’ll see how an existing application running on a VLAN can be seamlessly migrated to VCF Networking.
Once migrated, it becomes easy to enhance the application with additional services and benefits, such as:
- Load Balancing
- Micro-Segmentation for Enhanced Security
- Relocating Components of the Application to a New Building (even if that building doesn’t share the same VLANs)
- Resilience Against Building-Level Failures



